Research reveals that district investment in SEL implementation increased by around 45%, from $530 million to $765 million during the 2019–20 and 2020–21 school years.
The surge in interest in SEL amid a worldwide crisis that has affected everyone’s life is evidence of SEL’s effectiveness in fostering resilience in pupils and assisting them in overcoming obstacles. Despite this, there are several obstacles that educators must overcome to carry out interventions that aid in students’ social and emotional development. This post will discuss five of the most typical barriers to the mainstream adoption of SEL and offer some potential fixes.
What Is Social Emotional Learning?
The goal of the social-emotional learning (SEL) framework is to educate the whole kid. Instead of concentrating only on IQ, kids may also learn how to be emotionally intelligent. EQ is essential for success in life and is the foundation of a child’s welfare.
Source: hmhco.com
Through social and emotional development, kids learn how to control their emotions, become resilient, form wholesome relationships, and overcome obstacles in life. Research indicates that integrating SEL into the classroom can enhance academic results in addition to fostering good mental health.
Most Common Challenges You Can Face While Implementing SEL
Here are some of the biggest obstacles that might come your way and also the solutions to make your job easier:
1. Inadequate Knowledge
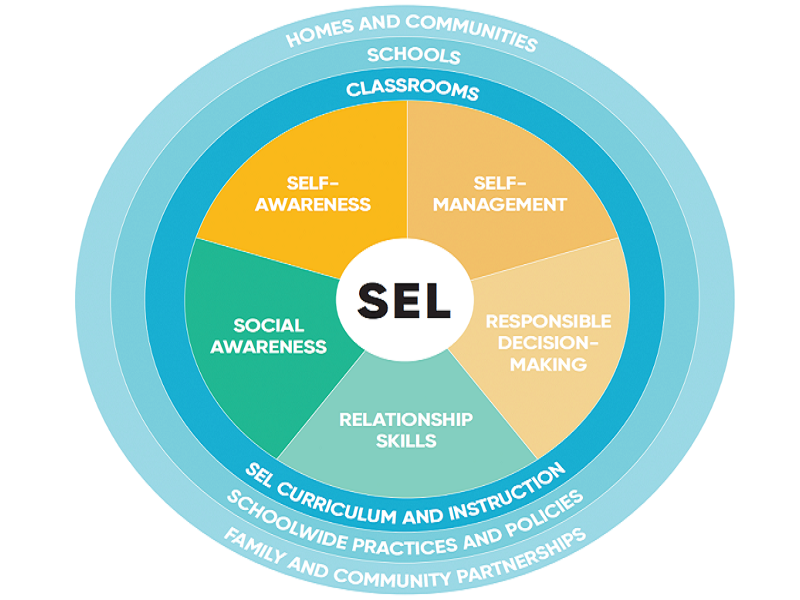
One of the most popular SEL frameworks is the CASEL (Collaborative for Academic, Social, and Emotional Learning) framework. It suggests the following five SEL key competencies:
- Self-management
- Self-awareness
- Relationship skills
- Social awareness
- Responsible decision-making skills
The Emotional Intelligence Model and 21st Century Skills are two more well-liked SEL models. Still, just 40% of teachers and 60% of district officials are aware of the most widely used SEL frameworks, which presents a barrier to adoption.
Possible Solution
To prevent the use of subpar or ineffectual SEL interventions, district executives, school principals, and teachers need to become more knowledgeable about SEL frameworks.
They may see the terminology, differences, and overlaps of the frameworks by comparing them. Understanding how different frameworks overlap can assist educators in developing a shared definition of SEL that guides the areas where their interventions should be concentrated.
2. Lack Of SEL Support System
Although the majority of educators find teaching social and emotional learning (SEL) to be enjoyable and valuable, organizing and preparing SEL activities takes time and can add to an already heavy burden for instructors.
Teachers who wish to adopt SEL must conduct additional study and preparation if they lack the required support, as SEL instruction frequently falls beyond the purview of regular professional teacher training. They may become discouraged and exhausted as a result of this.
Possible Solution
Leaders in schools and districts must figure out how to give SEL skill development for teachers a top priority.
For instance, by integrating a school-wide SEL solution schools have been able to develop the SEL competencies of their instructors and include SEL instruction into the curriculum. School administrators and district officials should work together to help schools in ensuring that teachers can implement SEL effectively.
3. No Proper Educator Skill Development
Many school districts don’t give professional development for teachers enough time or funding. This might be a result of their failure to recognize the vital significance of teachers’ personal social and emotional competency development.
However, if educators don’t practice what they preach and serve as positive role models for their pupils, how can we expect them to teach SEL effectively?
Possible Solution
District administrators should give adult SEL and well-being a top priority, aggressively promote it at the district and school levels, and give teachers access to materials and ongoing professional development opportunities.
Teachers should feel empowered and supported to voice issues and concerns in the classroom, and safe spaces should be provided for them to do so. Make employee well-being a priority by scheduling frequent staff meetings and one-on-one check-ins. Schools should search for methods to lessen the load on teachers who are feeling overburdened by the demand to apply SEL, or they can provide them with extra resources or training.
4. Personalisation vs Standardisation
Academic institutions frequently use standardization. Teachers should execute a curriculum with fidelity, or, to put it another way, run the program virtually exactly as intended, to get the greatest outcomes.
Academics benefit from standardization because it is the most effective means of achieving quantifiable outcomes through exacting evaluations. While evaluating SEL outcomes also requires some standardization, educators may find that this hinders their ability to customize SEL programs to the particular requirements of each district, school, and student.
Possible Solution
Developing strategies that provide customization within the constraints of instructional design may be necessary to strike a balance between uniformity and personalization.
Actively promoting culturally appropriate SEL may also be advantageous. This will guarantee that educators adhere to the standards while also allowing them to be adaptable to the many backgrounds, identities, and cultures represented in their classrooms.
5. Inability To Define Success
A further problem that teachers face is the absence of well-defined criteria for success in SEL. It might be challenging to standardize SEL success criteria across an entire school or district since there are so many distinct social-emotional learning frameworks accessible. Schools and districts are unable to choose which success measures to employ efficiently in the absence of such quantitative assessments.
Success measures include, for example:
- Student ability to maintain positive and foster new relationships
- Self-efficacy of the students
- Student’s ability to solve problems
- Student conflict resolution skills
- Student’s approaches to decision making
Possible Solution
Together with educators, school and district administrators should establish success indicators for their particular SEL initiatives.
This is significant since every school has unique students, needs, and objectives, all of which should be taken into consideration when establishing success criteria.
Overcome The Challenges And Teach ESL
The health, happiness, and academic achievement of your kids depend on you finding strategies to support teachers in implementing SEL programs utilizing pertinent and standards-aligned curricula. Apart from trying out the tips mentioned above you can also pursue online teacher training courses with certificates to gain a better knowledge about the various student needs and cater to them accordingly.



